Did you know that coffee is the second most traded commodity in the world, only surpassed by oil? As a coffee lover, I find this statistic fascinating and it highlights the immense economic significance of this beloved beverage. But have you ever wondered about the journey coffee takes from being a humble bean to the aromatic cup we enjoy each morning? In this discussion, we will explore the intricate economics behind the coffee industry, from the cultivation of coffee beans to the challenges of the global supply chain, and delve into the factors that influence coffee prices and consumer preferences. So grab your favorite brew and join me as we unravel the fascinating world of the economics of coffee.
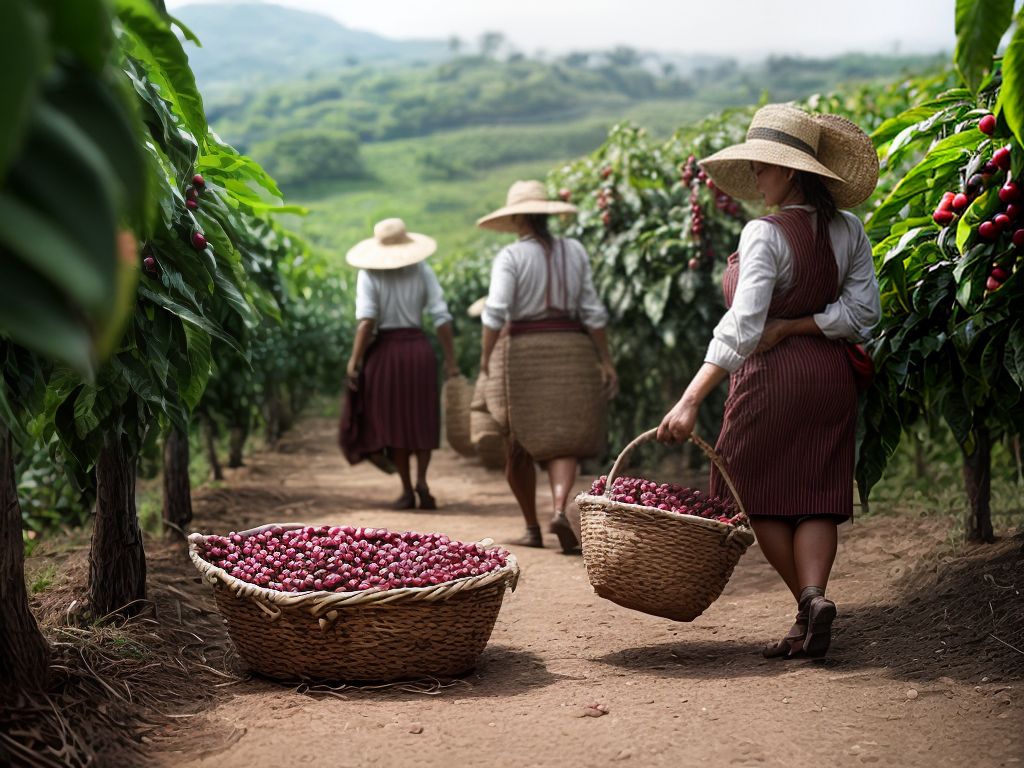
Coffee Bean Cultivation
Coffee bean cultivation involves carefully tending to the coffee plants, ensuring optimal growth and quality. The success of coffee bean cultivation depends on a combination of factors, including coffee bean genetics and organic farming methods.
Coffee bean genetics play a crucial role in determining the quality and flavor of the final product. Different coffee varieties have distinct characteristics, such as taste, acidity, and aroma. Through careful breeding and selection, growers can cultivate coffee plants with desirable traits, resulting in a superior cup of coffee. These genetic advancements have allowed for the production of unique and diverse coffee flavors, catering to the preferences of coffee enthusiasts worldwide.
Organic farming methods are also essential in coffee bean cultivation. Organic farming promotes the use of natural fertilizers and pest control methods, minimizing the use of synthetic chemicals. This approach not only protects the environment but also preserves the integrity of the coffee beans. Organic coffee is grown in harmony with nature, resulting in a rich and authentic taste that is highly sought after by conscientious consumers.
Harvesting and Processing Methods
Harvesting and processing methods are crucial steps in the coffee production chain, ensuring the preservation of flavor and quality from farm to cup. These methods have evolved over time, with advancements in technology and a focus on sustainability.
Mechanized harvesting is one method that has gained popularity in recent years. Traditionally, coffee cherries were handpicked, a labor-intensive process that required skilled workers. However, with the introduction of mechanization, large-scale coffee farms are now able to harvest cherries more efficiently. Mechanical harvesters use rotating drums or vibrating rods to shake the cherries off the trees, which are then collected in bins or bags. This method not only saves time and labor costs but also results in a more consistent harvest, as the machines can be programmed to pick only the ripe cherries.
On the other hand, natural processing techniques have also emerged as a way to enhance the flavor profile of coffee. In natural processing, the coffee cherries are left to dry with the fruit intact, allowing the sugars and flavors of the fruit to infuse into the coffee beans. This method is commonly used in regions with a dry climate, where the cherries can be spread out on patios or raised beds to dry naturally under the sun. The result is a coffee with a fruity and sometimes wine-like taste, which appeals to those seeking a unique and exotic flavor experience.
Fair Trade and Sustainable Practices
Implementing fair trade and sustainable practices in the coffee industry is essential for ensuring ethical production and environmental stewardship. Here are three key aspects to consider when it comes to ethical sourcing and minimizing the environmental impact of coffee production:
- Fair Trade Certification: Fair trade certification ensures that coffee farmers receive fair prices for their crops, allowing them to support themselves and their communities. By purchasing fair trade coffee, consumers can contribute to the well-being of farmers and promote social justice within the industry. This certification also guarantees environmental standards, such as prohibiting the use of harmful pesticides and promoting sustainable farming methods.
- Organic and Shade-Grown Coffee: Choosing organic and shade-grown coffee can significantly reduce the environmental impact of coffee production. Organic coffee is grown without synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, minimizing soil and water pollution. Shade-grown coffee is cultivated under the canopy of trees, providing habitat for migratory birds and preserving biodiversity. These practices promote sustainable agriculture and help mitigate climate change.
- Sustainable Packaging and Transportation: The coffee industry can further reduce its environmental impact by adopting sustainable packaging and transportation methods. Using eco-friendly materials for coffee packaging, such as compostable or recyclable materials, helps minimize waste. Additionally, opting for carbon-neutral transportation options, such as shipping via sailboats or using electric vehicles, can significantly reduce carbon emissions associated with coffee transportation.
Coffee Bean Pricing and Market Trends
After discussing the importance of fair trade and sustainable practices in the coffee industry, it is now crucial to examine the dynamics of coffee bean pricing and market trends. Coffee bean pricing is influenced by various factors, including supply and demand, weather conditions, and geopolitical events. To better understand the current market trends, let’s take a look at the table below:
| Year | Coffee Bean Futures Price (per pound) |
|---|---|
| 2016 | $1.20 |
| 2017 | $1.50 |
| 2018 | $1.10 |
| 2019 | $1.80 |
As we can see, coffee bean futures prices have fluctuated significantly in recent years. These price changes are driven by a combination of factors, such as changes in global production, shifts in consumer preferences, and speculation in the commodity markets.
Coffee bean trading, on the other hand, involves buying and selling coffee beans in the physical market. Traders, including coffee roasters and exporters, engage in this activity to secure their supply or take advantage of price differentials. The trading process involves negotiation, contracts, and logistics to ensure the beans are delivered on time and in the desired quality.
It is important to note that coffee bean pricing is not solely determined by the cost of production. Market dynamics and speculation play a significant role in shaping the prices. As a result, coffee farmers often face price volatility and uncertainty in their income.
Understanding the dynamics of coffee bean pricing and market trends is essential for all stakeholders in the coffee industry. By staying informed about market developments, we can make more informed decisions and work towards a sustainable and equitable coffee supply chain.
Global Coffee Production and Consumption
Global coffee production and consumption are key indicators of the industry’s health and overall market trends. Understanding the global coffee trade and coffee consumption trends is crucial for both coffee producers and consumers alike. Here are three important points to consider:
- Global coffee production: Coffee is grown in over 50 countries worldwide, with Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia being the top producers. The production of coffee is influenced by various factors, including climate conditions, disease outbreaks, and changes in consumer preferences. It is essential to track the global coffee production to assess the supply and availability of coffee in the market.
- Coffee consumption trends: Coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages globally, and its popularity continues to grow. With the rise of specialty coffee shops and the increasing demand for premium coffee, there has been a shift towards higher-quality and sustainable coffee products. Additionally, there has been a rise in coffee consumption in emerging markets such as China and India, contributing to the overall global consumption trend.
- Impact on the industry: The dynamics of global coffee production and consumption have a significant impact on the coffee industry. Fluctuations in production can affect coffee prices, leading to price volatility for both producers and consumers. Changes in consumption trends can also drive innovation and competition within the industry, as companies strive to meet the evolving preferences of coffee drinkers.
Coffee Roasting and Flavor Development
When it comes to coffee, the process of roasting plays a crucial role in developing its flavor. Different roasting techniques can yield a wide range of flavors, from light and fruity to dark and smoky. The level of roast also has a significant impact on the taste, with lighter roasts preserving more of the coffee’s original characteristics and darker roasts bringing out bolder, richer flavors. Understanding the intricacies of coffee roasting is essential for appreciating the diverse flavors that coffee has to offer.
Roasting Techniques and Flavors
To explore the diverse range of flavors in coffee, one must delve into the art of roasting and the various techniques employed to develop these nuanced taste profiles. Roasting is a crucial step in the coffee production process, as it transforms the green beans into the aromatic and flavorful beans we know and love. Here are three key aspects of roasting techniques and flavors:
- Roasting Levels: Different roasting levels, such as light, medium, and dark, result in distinct flavor profiles. Light roasts preserve the bean’s original flavors, while dark roasts develop bold and smoky notes.
- Roasting Time and Temperature: The duration and temperature at which coffee beans are roasted also influence the flavor. Shorter roasting times and higher temperatures result in brighter and fruitier flavors, while longer roasting times and lower temperatures yield deeper and richer flavors.
- Roasting Equipment: The choice of roasting equipment, such as drum roasters or hot air roasters, can affect the flavor development. Each type of roaster has its unique characteristics that contribute to the final taste of the coffee.
Understanding these roasting techniques and their impact on flavor profiles can enhance our appreciation of the complex and enticing world of coffee.
Impact of Roast Levels
As we explore the impact of roast levels on coffee flavor development, we can further appreciate the artistry behind roasting techniques and the intricate profiles they create. Roast level analysis plays a crucial role in determining the final flavor profile of the coffee. Different roast levels, ranging from light to dark, contribute to variations in taste, aroma, and body. Consumer preferences for roast levels can vary widely, with some preferring the bright acidity and delicate flavors of a light roast, while others enjoy the bold and rich flavors of a dark roast. Understanding consumer preferences is essential for coffee producers and roasters, as it allows them to tailor their offerings to meet the demands of their target market. By carefully selecting and controlling the roast level, coffee professionals can create unique and satisfying flavor experiences for coffee lovers around the world.
Packaging and Branding Strategies
When it comes to packaging and branding strategies in the coffee industry, there are several key points to consider. First, innovative packaging designs can help attract consumers and differentiate a brand in the market. Second, effective branding is crucial for creating a unique identity and building customer loyalty. Lastly, sustainable packaging solutions are becoming increasingly important as consumers prioritize environmentally friendly options. By focusing on these points, coffee companies can enhance their packaging and branding strategies to stay competitive in the market.
Innovative Packaging Designs
In the world of coffee, innovative packaging designs play a crucial role in capturing consumers’ attention and enhancing brand recognition. With the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions, coffee companies are investing in unique and environmentally friendly designs. Here are three innovative packaging designs that are making waves in the industry:
- Biodegradable Coffee Pods: Companies are introducing biodegradable coffee pods made from plant-based materials. These pods reduce the environmental impact of single-use packaging and provide a guilt-free coffee experience.
- Minimalist Packaging: Some brands are adopting a minimalist approach to packaging, using simple designs and eco-friendly materials. This not only reduces waste but also creates a sleek and modern aesthetic that appeals to consumers seeking a sustainable lifestyle.
- Reusable Containers: Coffee companies are exploring the concept of reusable containers, allowing customers to purchase coffee in refillable jars or canisters. This not only reduces packaging waste but also fosters a sense of community and belonging among consumers who are committed to sustainable practices.
Branding for Market Differentiation
The focus on innovative packaging designs in the coffee industry extends beyond sustainability, now encompassing branding strategies that aim to differentiate companies in the market. Packaging design plays a crucial role in attracting consumers and creating a distinct identity for coffee brands. Companies are using creative and eye-catching packaging designs to stand out on store shelves and enhance their brand image. From unique shapes and colors to eco-friendly materials, packaging design has become an integral part of marketing strategies. By incorporating elements that resonate with the target audience, such as minimalist designs or vibrant colors, companies can effectively communicate their brand values and create a sense of belonging for consumers. In a highly competitive market, effective branding through packaging design is essential for companies to establish themselves and gain a competitive edge.
Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Sustainable packaging solutions are becoming increasingly prevalent in the coffee industry as companies prioritize environmental consciousness in their branding strategies. With the growing concern over the environmental impact of packaging waste, coffee companies are seeking innovative packaging solutions that are both functional and sustainable. Here are three examples of sustainable packaging solutions in the coffee industry:
- Compostable Packaging: Coffee companies are exploring the use of compostable packaging made from renewable materials such as plant-based plastics. This allows the packaging to break down naturally, reducing waste and minimizing environmental harm.
- Recyclable Packaging: Many coffee companies are opting for recyclable packaging made from materials such as aluminum or cardboard. These materials can be easily recycled, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
- Reusable Packaging: Some coffee companies are introducing reusable packaging options, such as refillable coffee containers or coffee pods. This encourages customers to reduce their environmental impact by using the same packaging multiple times.
Coffee Distribution Networks
Coffee distribution networks play a crucial role in the global economy and supply chain. As the demand for coffee continues to rise, the distribution of this beloved beverage faces various challenges. One of the main challenges is the complex nature of the coffee supply chain, which involves numerous intermediaries and long distances between coffee-growing regions and consumer markets.
One of the key trends in coffee distribution is the increasing focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions, leading to a demand for coffee that is produced and distributed in an environmentally and socially responsible manner. This has prompted coffee companies to invest in sustainable distribution practices, such as utilizing more eco-friendly packaging materials and working directly with farmers to ensure fair trade practices.
Another trend in coffee distribution is the growing popularity of e-commerce platforms. Online coffee retailers have emerged as a convenient and accessible way for consumers to purchase their favorite brews. These platforms offer a wide range of coffee varieties, flavors, and origins, allowing consumers to explore and experiment with different options. Additionally, e-commerce eliminates the need for physical stores, reducing overhead costs and enabling coffee companies to reach a larger customer base.
Coffee Shop Economics
As a business owner in the coffee industry, I understand the importance of pricing strategies and supply chain management in coffee shop economics. Pricing strategies play a crucial role in attracting customers and maximizing profits, while effective supply chain management ensures a steady and reliable flow of coffee beans and other essentials. By carefully considering these factors, coffee shop owners can optimize their operations and thrive in a competitive market.
Pricing Strategies
In order to maximize profitability, coffee shops employ various pricing strategies that cater to consumer demand and market trends. These strategies take into account factors such as roasting techniques and coffee distribution. Here are three pricing strategies commonly used in coffee shops:
- Premium Pricing: Coffee shops can set higher prices for their specialty or premium coffees, which are often made using unique roasting techniques or sourced from specific regions. This strategy targets customers who are willing to pay a premium for high-quality and unique coffee experiences.
- Value Pricing: Some coffee shops adopt a value pricing strategy by offering lower prices for their regular menu items. This attracts price-sensitive customers and encourages them to choose the coffee shop over competitors.
- Bundle Pricing: Coffee shops can also offer bundle pricing, where they combine multiple items or services at a discounted price. For example, they may offer a breakfast bundle that includes a coffee and a pastry at a lower total price than if these items were purchased separately.
Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is crucial for coffee shops to ensure the timely delivery of high-quality coffee beans and other necessary ingredients. It involves the coordination of activities from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product to customers. One important aspect of supply chain management in the coffee industry is the implementation of fair trade certification and ethical sourcing practices. Fair trade certification ensures that coffee farmers receive a fair price for their labor, while ethical sourcing guarantees that the coffee beans are produced in an environmentally and socially responsible manner. By incorporating these practices into their supply chain, coffee shops can not only support sustainable and ethical practices but also attract customers who value these principles. This, in turn, contributes to building a loyal customer base and enhancing the overall reputation of the coffee shop.
Specialty Coffee and the Third Wave Movement
With the rise of the specialty coffee movement, coffee enthusiasts are embracing a new wave of craftsmanship and quality in their daily brew. As a coffee lover myself, I have witnessed the transformation in the coffee industry as it shifts towards a focus on specialty coffee. Here are three key aspects that define this movement:
- Direct Trade Relationships: Specialty coffee is often sourced through direct trade relationships between coffee farmers and roasters. This allows for a more transparent and mutually beneficial partnership, where farmers receive fair compensation for their high-quality beans. By eliminating intermediaries, direct trade promotes sustainability and ensures the economic viability of coffee farming communities.
- Quality Control: In the world of specialty coffee, quality control is paramount. From the moment the coffee cherries are harvested to the final cup, rigorous protocols are in place to maintain consistent excellence. This includes meticulous sorting, processing, and roasting techniques. Quality control measures ensure that only the finest beans make it into your cup, resulting in a more refined and enjoyable coffee experience.
- Cupping Protocols: Cupping is the standardized tasting method used by specialty coffee professionals to evaluate the flavor, aroma, and overall quality of coffee. This systematic approach involves slurping coffee from a spoon and assessing its various attributes. Cupping sessions allow roasters, buyers, and enthusiasts to identify flavor profiles, detect defects, and make informed decisions about the beans they source.
In the third wave of coffee, specialty coffee has become a way to connect with a global community of coffee lovers who appreciate the artistry and dedication that goes into each cup. By embracing direct trade relationships, quality control, and cupping protocols, we are not only elevating our own coffee experience but also supporting a more sustainable and ethical coffee industry. So, let’s raise our mugs to the third wave and savor the delicious journey of specialty coffee.
Coffee Industry Regulations and Certifications
As the specialty coffee movement gains momentum, it is important to understand the regulations and certifications that shape the coffee industry. These regulations and certifications play a crucial role in ensuring the quality, sustainability, and fair trade practices within the coffee supply chain.
One of the key regulations in the coffee industry is the International Coffee Agreement (ICA). The ICA is an international treaty that aims to promote a sustainable coffee economy and ensure stability in the coffee market through cooperation among coffee-producing and coffee-consuming countries. It provides a framework for the negotiation of coffee prices, market transparency, and the promotion of sustainable coffee production practices.
In addition to regulations, certifications also play a vital role in the coffee industry. One of the most well-known certifications is Fairtrade. Fairtrade certification ensures that coffee farmers receive fair prices for their produce, enabling them to invest in their communities and improve their livelihoods. It also guarantees fair working conditions and environmental sustainability throughout the supply chain.
Another important certification is the Rainforest Alliance. This certification focuses on promoting sustainable farming practices that protect biodiversity, conserve natural resources, and improve the livelihoods of coffee farmers. Coffee with the Rainforest Alliance certification ensures that it has been produced in accordance with rigorous environmental and social standards.
Other certifications such as Organic, UTZ, and Direct Trade also exist, each with its own set of standards and requirements. These certifications provide consumers with confidence that the coffee they are purchasing meets certain quality, ethical, and sustainability standards.
Coffee Supply Chain Challenges
As a coffee enthusiast, I understand that the coffee supply chain faces several challenges. One major challenge is logistics and transportation, as coffee beans need to be transported from remote regions to processing facilities and then to consumers around the world. Another challenge is price volatility, as factors such as weather conditions and market demand can cause fluctuations in coffee prices. Lastly, sustainability efforts are crucial in addressing issues such as deforestation, water usage, and fair trade practices within the coffee supply chain.
Logistics and Transportation
The challenges faced in the logistics and transportation of coffee within the supply chain require careful planning and efficient execution. To optimize the logistics of coffee transportation and minimize costs, several key factors must be considered:
- Infrastructure: The condition of roads, ports, and warehouses along the coffee supply chain can greatly impact transportation efficiency. Investing in infrastructure improvements can reduce transportation delays and costs.
- Supply chain visibility: Having real-time visibility into the location and status of coffee shipments can help identify bottlenecks and optimize transportation routes. Utilizing technologies like GPS tracking and data analytics can enhance supply chain visibility.
- Collaboration and coordination: Effective communication and coordination among all stakeholders in the coffee supply chain, including farmers, exporters, importers, and transportation providers, are essential for smooth logistics operations. Collaboration can help streamline processes, reduce delays, and ultimately lower transportation costs.
Price Volatility
Price volatility in the coffee supply chain poses significant challenges for all stakeholders involved. One of the key factors contributing to this volatility is price speculation, which can greatly impact the coffee industry. Price speculation refers to the practice of predicting and betting on future price movements in the coffee market. This can lead to significant fluctuations in coffee prices, making it difficult for producers, traders, and consumers to plan and budget effectively. Another factor that contributes to price volatility is the trading of coffee futures. These are contracts that allow buyers and sellers to agree on a future price for coffee, which can be influenced by various factors such as weather conditions and global demand. The uncertainty surrounding these futures contracts can further exacerbate price fluctuations in the coffee market, creating challenges for all participants in the supply chain.
Sustainability Efforts
In addressing the challenges within the coffee supply chain, sustainability efforts play a crucial role. Sustainable farming practices are essential in reducing the environmental impact of coffee production. Here are three key aspects of sustainability efforts in the coffee industry:
- Conservation of natural resources: Sustainable farming practices focus on minimizing water usage, protecting soil health, and preserving biodiversity. This helps maintain the long-term viability of coffee farms and protects the surrounding ecosystems.
- Climate change mitigation: Coffee farming is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events and shifting growing conditions. Sustainable practices aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through practices like shade-grown coffee cultivation and carbon sequestration.
- Social responsibility: Sustainability efforts also encompass fair labor practices and equitable economic opportunities for coffee farmers. This includes ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and empowering local communities.
Coffee Market Volatility and Price Fluctuations
Due to its global demand and the influence of various factors, the coffee market experiences significant volatility, leading to frequent price fluctuations. The coffee market is highly susceptible to changes in supply and demand, as well as external factors such as weather conditions, political instability, and economic trends. These fluctuations can have a significant impact on the price of coffee, making it a highly volatile commodity.
One of the key factors that contribute to the volatility in the coffee market is the demand for coffee. Coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages in the world, with millions of people relying on it to start their day. As a result, any changes in coffee consumption patterns can have a direct impact on the market. For example, if there is a sudden increase in demand for coffee, it can lead to a shortage in supply, causing prices to rise. Conversely, if there is a decrease in demand, it can result in an oversupply of coffee, leading to a decrease in prices.
In addition to changes in demand, coffee trading futures also play a significant role in market volatility. Coffee futures are contracts that allow buyers and sellers to agree on a price for coffee at a future date. These futures contracts are traded on exchanges, and their prices are influenced by a variety of factors, including market sentiment, speculation, and economic indicators. As a result, fluctuations in coffee futures prices can have a direct impact on the spot price of coffee.
Consumer Preferences and Market Segmentation
With the understanding that consumer preferences heavily influence the demand for coffee, it is essential to explore how these preferences contribute to market segmentation. Market segmentation refers to the process of dividing a market into distinct groups of consumers who share similar characteristics and preferences. Understanding consumer behavior and market segmentation is crucial for coffee producers and retailers to effectively target their products and marketing strategies.
- Demographic Segmentation: One way to segment the coffee market is based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, and occupation. For example, younger consumers might prefer specialty coffee blends and are willing to pay a premium for ethically-sourced beans. On the other hand, older consumers might prefer traditional coffee flavors and value affordability.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Another approach to market segmentation is based on psychographic factors, such as lifestyle, values, and personality traits. Some consumers might be health-conscious and prefer organic or decaffeinated coffee options. Others might be adventurous and seek unique flavor profiles from different coffee origins.
- Geographic Segmentation: Geographic segmentation takes into account the geographical location of consumers. Preferences for coffee can vary across regions due to cultural influences and local coffee traditions. For instance, consumers in South America might have a preference for dark-roasted, strong coffee, while consumers in Europe might favor lighter roasts.
The Future of the Coffee Industry
The coffee industry is poised for significant growth and innovation in the coming years. As global demand for coffee continues to rise, companies are exploring new avenues for future innovations and expanding into emerging markets.
One major area of focus for the future of the coffee industry is sustainability. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their choices, and coffee companies are taking steps to address these concerns. From implementing eco-friendly farming practices to developing more sustainable packaging options, the industry is working towards a greener future.
Another key trend in the future of the coffee industry is the rise of specialty coffee. Consumers are becoming more interested in unique and high-quality coffee experiences, leading to an increased demand for specialty beans and brewing methods. This has created opportunities for small-scale coffee producers and boutique coffee shops to thrive in the market.
In addition, technology is playing a significant role in shaping the future of the coffee industry. From mobile ordering apps to smart coffee machines, technological advancements are making it easier than ever for consumers to enjoy their favorite cup of joe. These innovations are not only improving the customer experience but also streamlining operations for coffee businesses.
Furthermore, the emerging markets present a promising future for the coffee industry. As coffee consumption continues to grow in countries such as China, India, and Brazil, companies are expanding their operations to tap into these new markets. This not only opens up new opportunities for coffee producers but also helps to diversify the global coffee market.